Build this DIY Intruder Alarm System using cheap off-the-shelf components. It has automatic Exit and Entry delays, a timed Bell Cut-off. Use it in your Home - Business Premises - Garage - Workshop - Shed etc. It has provision for normally-open and normally-closed switches and will accommodate the usual input devices (Pressure Mats, Magnetic-Reed contacts, Foil Tape, Movement Detectors and Inertia Sensors).
Cmos Single-Zone Alarm - Support Material
Introduction
The prototype of the Cmos Single-Zone Alarm was built using only the Stripboard Layout as a guide. So - if you have faithfully reproduced that layout - you will have a working circuit.
Once you're satisfied that your layout is correct - and you have made a careful and thorough check of the underside of the board - it's time to power-up the circuit and test its operation. This is always an anxious moment. If you construct a lot of circuits - you might consider building the
Current Limiting Power Supply - or alternatively - you could add the Simple Current Limiter to your existing PSU. Both will let you set an upper limit on the amount of current supplied to your circuit - and so protect it from any serious damage.
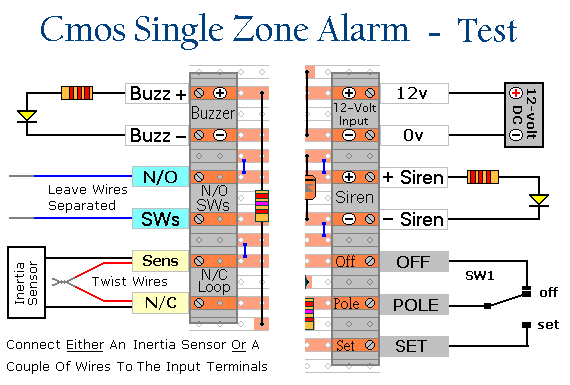
Setup
You can simulate the trigger-switches using short lengths of flexible multi-stranded wire - such as alarm cable. But if you want to check the sensitivity adjustment - you'll need to connect an inertia-sensor to the input terminals. A couple of LEDs and resistors are all that's needed to demonstrate that the Siren and Buzzer outputs are working properly.
If You Find a Problem
If - in the course of the test - you find that something is not working properly, then a careful inspection of the relevant area of the circuit board should turn up the cause of the problem. If an LED is not lighting - check that it's connected the right way round. Where you've cut the board to size - look for small loose strands of copper left behind by the saw. Check the board for short-circuits caused by component leads touching each other. It can also happen that the stripboard itself is faulty. I have seen cases where the copper tracks have not been completely severed from one another during manufacture.
If you've built your circuit using the specified components - and you've followed the step-by-step construction guide described on the Cmos Single-Zone Alarm Support Page - then the chances are that any bug will be caused by something minor - a component connected the wrong way round - a missing or unwanted solder bridge - an incomplete cut in the track etc. If you haven't used the specified transistors - check the pin configuration. Just because the transistors look the same - do not assume that they have the same pin configuration.
If you can't see anything obvious then adopt a systematic approach to faultfinding. Simply replacing components at random is rarely successful. Begin by double-checking that all of the cuts in the tracks have been made - that they are all In The Right Place - and that they sever the track completely. Use a magnifying glass - and backlight the board. It only takes the smallest strand of copper to cause a problem.
When you're satisfied that the tracks have been severed in all the right places, check that you have made and correctly placed all 10 solder bridges - 11 if you've used the smaller preset. Mark each bridge with a felt-tip pen - or something similar - so that it can be easily identified later.
Next - carefully examine the full length of each track. Use a magnifying glass - and backlight the board. Look for unwanted solder bridges. Your felt-tip markings will tell you which ones should be there - and help you identify any that shouldn't be there.
If all else fails and you still haven't found the cause of the problem - work your way through the assembly instructions on the Support Page. Check each individual component and link - to make sure that it's present and correctly positioned.
Print out the drawings and mark off the components as you go. Pay particular attention to the orientation of the transistors, diodes and electrolytic capacitors. Take your time and examine each individual component carefully.
Click Here For A Photograph Of The Prototype.
 SUGGESTIONS
SUGGESTIONS